Micro water pumps supplier
It's incredibly frustrating when your diaphragm water pump is plugged in and humming but not producing water. Whether it is used for fish tank, coffee machines, medical equipment or device, the fault will influence the operation of the whole system.
Don't worry, the structure and principle of the diaphragm pump are relatively simple, and most failures can be found and solved through systematic inspection.This article will guide you step by step to diagnose the problem, from the easiest to the hardest.
First, understand how a diaphragm pump works
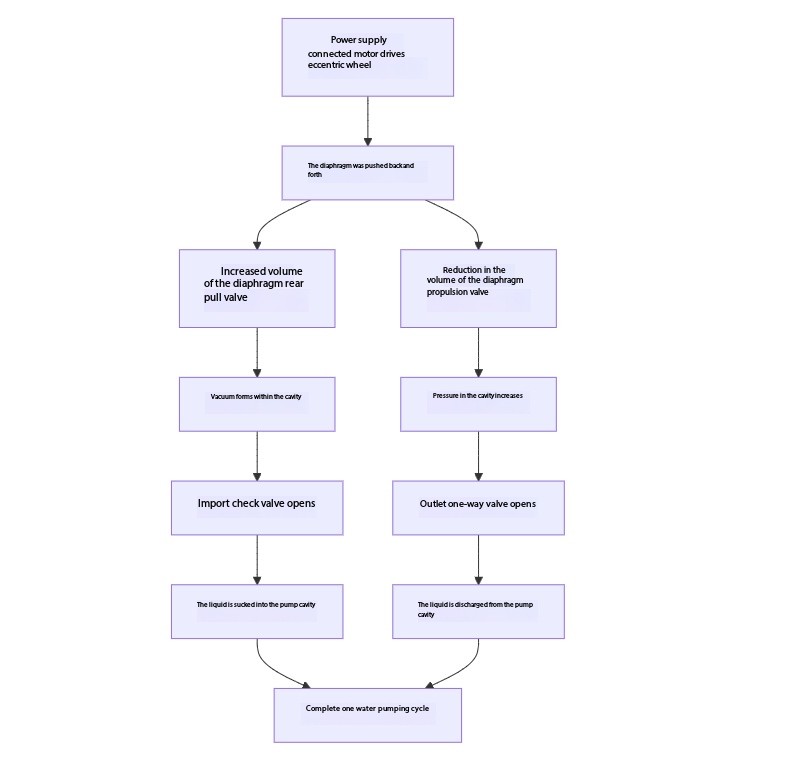
Before you start your investigation, understanding the fundamentals will make it easier. The core working process of the diaphragm water pump is as follows:
In simple terms, it is a through the diaphragm reciprocating motion, and cooperate with the import and export of two one-way valve, like a "breathing" periodically suction and discharge process of liquid. Any problem in any link may lead to the failure to pump water.
Step 1: Basic investigation (not problems with the pump body itself)
These are the most common and easily fixed problems, accounting for about 70% of the causes of failures.
Power and connection issues:
Check the power supply: Ensure that the rated voltage of the pump matches the power supply voltage.Use a multimeter to measure whether the power supply is available and whether the output voltage is normal.
Check the wiring: Check whether the connection of the power cord, plug and controller (such as PWM governor) is firm and there is no open circuit or virtual connection.
Water source and pipeline problems
Is the liquid source sufficient?Check whether the source tank is short of water and whether the inlet is exposed to air.
Is the water inlet pipe clogged? Disassemble the water inlet pipe and check if there are any foreign objects, scale or impurities blocking it.
Is the pipe bent or flattened? Make sure that especially the inlet hose is not severely bent or flattened, which may affect the flux.
Pump body is higher than the liquid level? If the liquid level is lower than the pump's inlet, "Priming" is required. Although diaphragm pumps have a certain self-priming ability, if the liquid level difference is too large, it will result in the inability to draw water.Try to empty the air by placing the pump below the liquid level or reverse filling the liquid from the outlet.
The issue of air tightness (the most crucial!)
Check all joints: The diaphragm pump sucks water by negative pressure. Any slight air leakage at the water inlet end will completely destroy its self-priming ability. Make sure that all pipe joints and sealing rings are tightened and in good condition.
Quick test: Immerse the water inlet directly in water, or hold the water inlet tightly with your hand and start the pump to feel if there is obvious suction. If there is no suction, the problem is likely with the pump itself.
Step 2: Check the pump body itself
If the first step is OK, then we need to go deeper into the pump body.
Blockage of foreign matter (commonly seen in new pumps or poor operating environment)
The problem: The flow channels and valve ports inside the pump may be blocked by debris, scale or particles in the delivery liquid left during installation.
Solution: Disassemble the pump head and carefully rinse all flow channels and valve assemblies with clean water or an air gun.
Check valve failure (the most common mechanical failure)
Working Principle: The diaphragm pump has an inlet check valve and an outlet check valve, which only allow liquid to pass in one direction. If either valve is stuck, damaged or not sealed tightly, the pump will not be able to establish a pressure differential, resulting in "only sound but no pumping".
How to judge:
Inlet valve failure: pump unable to absorb water, no suction.
Outlet valve failure: The pump may have suction, but the water output is weak or not at all, and even the liquid may flow back after the machine stops.
Solution: Take apart the pump head and check the two check valves (usually rubber umbrella valve/duck mouth valve or ball valve) for foreign body stuck, deformation, aging loss of elasticity.To clean or replace.
The diaphragm is damaged
The diaphragm is a core moving component. After long-term reciprocating operation, it may become fatigued, aged or cracked due to corrosion by chemical liquids.
Results: Once the diaphragm is broken, the pump chamber cannot form an effective sealing space, and the mouth chamber is colluded, and the pumping ability is completely lost.
How to determine: After disassembly, directly check if the diaphragm has any perforations or tears.
Solution: Replace the diaphragm with a new one.
Failure of drive mechanism
Motor Burnt: If the pump is completely silent, or has a burning smell when powered on, the motor is likely burned out. Use a multimeter to measure the motor resistance to determine if this is the case.
Gear/link mechanism damage: For a pump driven by a deceleration motor, the internal plastic gear or link may break due to overload or fatigue, causing the motor to turn but the diaphragm to not move. Disassembly and inspection are required.
Conclusion: Systematic screening process
You can follow the flowchart below to quickly locate the problem
Phenomenon: Pump running but no water
Listen to the sound and feel the vibration: Is the pump operating normally?
No -> Check the power supply, circuits and motor.
Yes -> Proceed to the next step.
Check the suction power: Disconnect the water inlet pipe, tightly block the water inlet of the pump with your hand, and then start it.
No obvious suction is felt -> The problem is most likely with the pump body itself. Enter Step 3.
There is a strong suction force -> The problem lies before the pump body.Check the water source, intake line, filter for blockage, and all intake joints for air leakage.
Pump body itself inspection (disassembly required)
a. Check whether the flow channel and one-way valve are blocked by foreign bodies.
b. Check whether the inlet and outlet check valves are damaged, deformed or not sealed tightly.
c. Check whether the diaphragm is damaged.
d. Check whether the drive mechanism (gears, connecting rods) is damaged.
Through the above thorough investigation from the surface to the core and from the simple to the complex, you can basically solve over 95% of the problems of diaphragm water pumps not pumping water. Remember, air tightness, check valves and diaphragms are the top priorities in the inspection. If you do not have the conditions for disassembly or the problem persists after inspection, it is recommended that you contact professional technicians or the supplier for repair.
you like also all
Post time: Oct-28-2025